Geekflare is supported by our audience. We may earn affiliate commissions from buying links on this site.
The terms URI, URL, and URN are the most used when it comes to the internet and web terminology.
Let’s take a closer look to understand the difference between them.
Uniform Resource Locator
A URL is a string of characters used to access the information or a resource by using the address of the resource location.
Syntax of URL
scheme: subdomain/domain-name.Top-level-domain/sub-folderIn this syntax, the scheme provides details about the protocol in use like HTTPS, FTP, and HTTP. The subdomain element is not mandatory. After that, it has a second-level domain, which is the domain address. And finally, the subfolder, if there is any, takes the user to the exact target location.
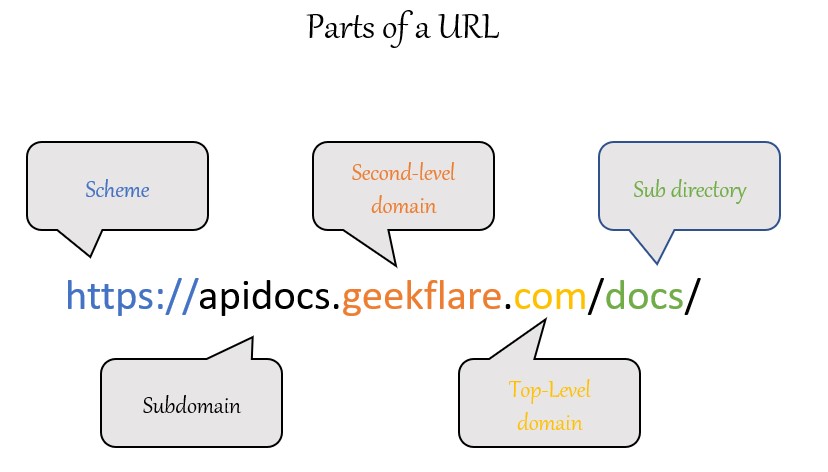
Example of URL
https://www.geekflare.com/articles
mailto:[email protected]
file:///localhost/8.8.8.8Uniform Resource Name
Uniform Resource Name does not offer the protocol used to access the resource or the resource’s address, but it does provide information about the resource itself. It includes only the name or identification of the resource.
Syntax of URN
urn::Each URN consists of at least three parts.
- The scheme specification is the first part of the URN.
- Following urn, namespace identifier (NID) should be present, which must be registered with IANA like nbn, uuid, etc.
- Finally, the namespace-specific string (NSS) which precisely identifies the item.
Example of URN
urn:nbn:de:101:3-2019075675872913
urn:uuid:6r4bc420-9c3a-12i9-97d9-0665700c9a66
ISBN 1-446-2776877-40ISBN – Unique identifier for books
Uniform Resource Identifier
A URI is a standard method for identifying resources on the internet by their location, name, or both. URN and URL together are known as URI.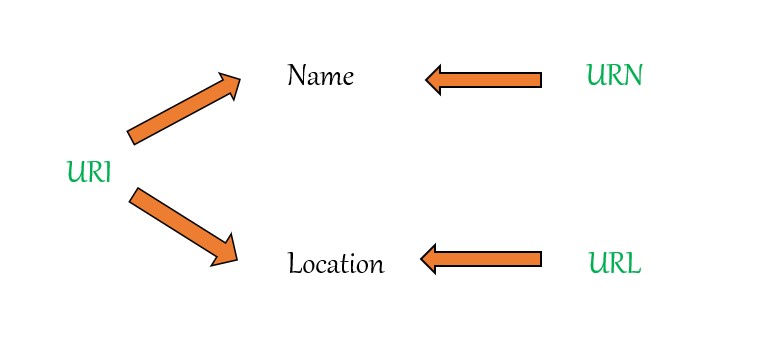
Syntax of URI
scheme:// authority path ? query # fragmentIn this syntax, the scheme provides details about the protocol in use. Authority attribute identifies the domain address. The path attribute displays the resource’s whole path, and the query represents a request action. And finally, the partial component of a resource is referred to as a fragment.
Example of URI
foo://webiste.com:8042/over/there?name=ferret#nose
https://mywebsite.com/drive/photosEvery syntax element isn’t mandatory in a URI all the time. It only requires a scheme name and a file path mainly.
mailto:[email protected]
Name: Mary Jane
ISBN 1-446-2776877-40
telnet://192.0.1.24/80Note – All URLs are URI. But not every URI comes under URL
Conclusion
I hope you have gained a better understanding of URI, URL, and URN. You may also be interested in reading about the URL blacklist and how to fix it.



