
As Ubuntu users, we might want to know if we are the only ones using our network, especially wi-fi, or are there any other unwanted users leeching on our network bandwidth. This skill also comes in handy when we want to be sure that any hacker is not accessing our system by being connected to our network.
Scan your network with Nmap on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS
This article describes a step by step procedure to use the Nmap tool that gives you a list of all devices connected to your network.
We have run the commands and procedures mentioned in this article on a Ubuntu 20.04 LTS system.
Step 1: Open the Ubuntu command line
We will be using the Ubuntu command line, the Terminal, in order to view the devices connected to our network. Open the Terminal either through the system Dash or the Ctrl Alt T shortcut.
Step 2: Install the network scanning tool Nmap
When it comes to reliable network scanning, Nmap is a tool that you can totally depend on.
Enter the following command as sudo in the Terminal application in order to install the tool.
The system will ask you the password for sudo as only an authorized user can install/uninstall and configure software on Ubuntu.
The system will also prompt you with a y/n option to confirm the installation. Please enter Y and hit enter to begin the installation process.
Step 3: Get the IP range/subnet mask of your network
In order to know which devices are connected to your network, you first need to get the IP range or the subnet mask of your network. We will be using the ifconfig command in order to get this IP. In order to run the ifconfig command, we need to have net-tools installed on our Ubuntu. Use the following command in order to install net-tools if you already do not have it installed on your system:
$ sudo apt install net-tools
The system will prompt you with a y/n option to confirm the installation. Please enter Y and hit enter to begin the installation process.
Once you have the net-tools utility available, run the following command in order to get information about the network(s) your system is connected to:
$ ifconfig
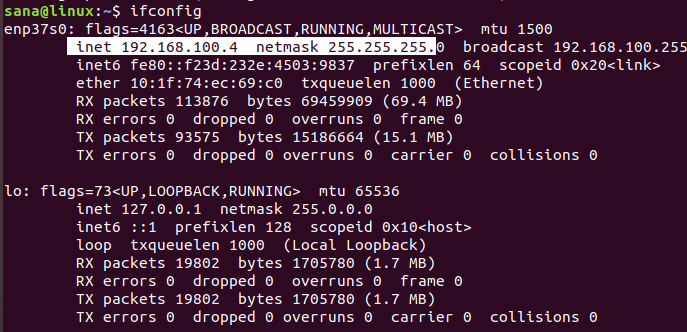
The highlighted IP from the output indicates that our system is using 192.168.100.0 subnet mask and the range is 255. Thus our network IP range is from 192.168.100.0 to 192.168.100.255.
Alternative (UI)
Instead of using the ifconfig tool, you can get the subnet mask IP through the Ubuntu GUI as well.
Access the Settings utility from the system Dash and check the details of your network either by clicking the settings icon against the wifi or ethernet network you are connected to.
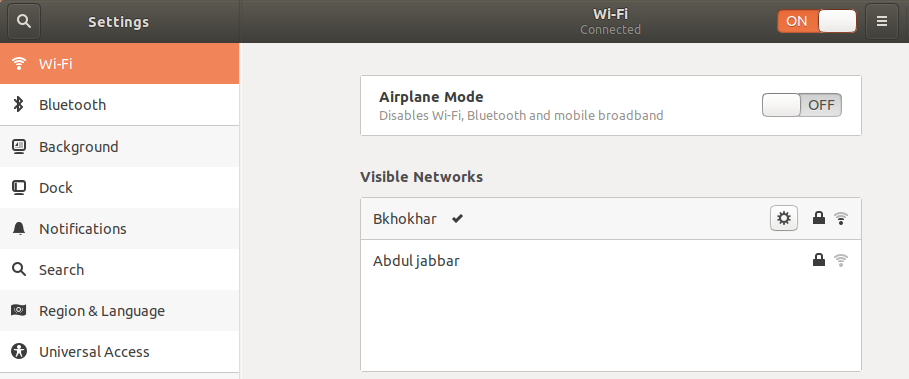
In this example, we have checked the settings of a wi-fi network we are currently connected to.
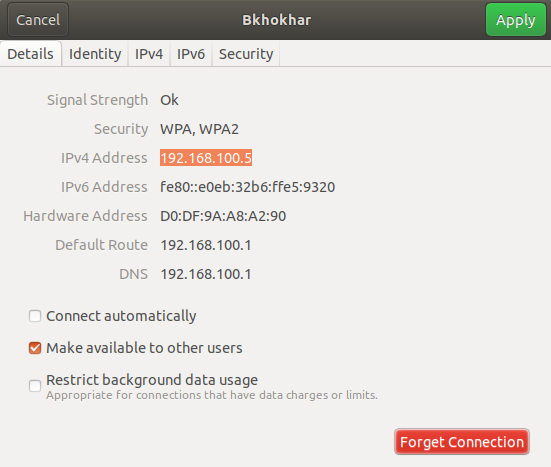
The highlighted ipv4 address or the Default Route address indicates that we are connected to a subnet IP 192.168.100.0
Step 4: Scan network for connected device(s) with Nmap
Through the Nmap tool, you can scan the report of all devices connected to a network by providing the subnet mask IP as follows:
$ nmap -sP 192.168.100.0/24
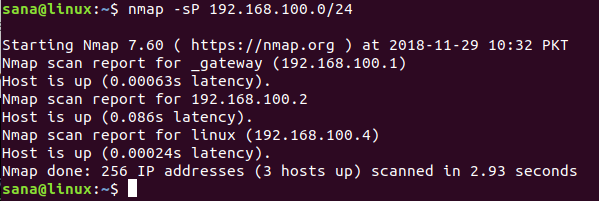
The output shows that there are 3 devices connected on the network; one is the router itself, one is the Linux system I am using on my laptop, and the third one is my phone.
Step 5: Exit the Terminal
Use the following command in order to exit the Terminal application after you are done with extracting the required information:
$ exit
In this article, you have learned how an Ubuntu user can install and use the Nmap command. We showed you how to view which devices are connected to the network he/she is using. This way you can verify that no unauthorized device is connected to your network.



