This is part 10 in the CentOS 8/RHEL 8 mail server from scratch tutorial series. In this article, I will show you how to use Amavis and ClamAV to scan viruses in email messages.
Amavis (A Mail Virus Scanner) is a high-performance interface between a message transfer agent (MTA) such as Postfix and content filters. A content filter is a program that scans the headers and body of an email message, and usually takes some action based on what it finds. The most common examples of content filters are ClamAV virus scanner and SpamAssassin.
Amavis speaks standard SMTP protocol and can also use the Sendmail milter interface. It’s commonly used for
- virus-scanning by integrating with ClamAV (Clam AntiVirus)
- spam-checking by integrating with SpamAssassin
- DKIM signing and verification. (Actually, I prefer to use OpenDKIM for DKIM signing and verification.)
Prerequisites
You should have completed at least part 1 (Postfix SMTP server) and part 2 (Dovecot IMAP server) of the CentOS 8/RHEL 8 mail server from scratch tutorial series. Note that if you used iRedMail or Modoboa to set up your mail server, then Amavis and ClamAV are already installed and configured, so you don’t need to follow this tutorial.
Warning: Amavis and ClamAV require a fair amount of RAM. Make sure you have at least 1.3 GB of free RAM on your server before installing Amavis and ClamAV. The whole mail server stack (Postfix, Dovecot, Amavis, ClamAV, SpamAssassin, OpenDKIM, MySQL/MariaDB, PostfixAdmin, and Roundcube Webmail) needs at least 3 GB RAM to run smoothly. If your RAM runs out, you are going to have troubles like mail server going offline or unresponsive.
Step 1: Install Amavis on CentOS 8/RHEL 8
Amavis is written in Perl. We need to enable the EPEL (Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux) and CodeReady Linux Builder repository on RHEL 8 to install some Perl dependencies for Amavis.
sudo dnf install epel-release sudo subscription-manager repos --enable=codeready-builder-for-rhel-8-x86_64-rpms
On CentOS 8, enable the EPEL (Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux) and PowerTools repository to install Perl dedpendencies for Amavis.
sudo dnf install epel-release -y sudo dnf config-manager --set-enabled PowerTools
Then install the amavis package.
sudo dnf install amavis -y
To check the version number, run
amavisd -V
Sample output:
amavisd-new-2.12.0 (20190725)
Viruses are commonly spread as attachments to email messages. Install the following packages for Amavis to extract and scan archive files in email messages such as .7z, .cab, .doc, .exe, .iso, .jar, and .rar files.
sudo dnf -y install arj bzip2 cpio file gzip nomarch spax unrar p7zip unzip zip lrzsz lzip lz4 lzop
Note that if your server doesn’t use a fully-qualified domain name (FQDN) as the hostname, Amavis might fail to start. And the OS hostname might change, so it’s recommended to set a valid hostname directly in the Amavis configuration file.
sudo nano /etc/amavisd/amavisd.conf
Find the following line.
$mydomain = 'example.com'; # a convenient default for other settings
It’s also recommened to change the default mydomain value to your own domain name.
$mydomain = 'linuxbabe.com'; # a convenient default for other settings
Then find the following line.
# $myhostname = 'host.example.com'; # must be a fully-qualified domain name!
Remove the first comment character (#) and change host.example.com to the hostname of your mail server like below.
$myhostname = 'mail.linuxbabe.com'; # must be a fully-qualified domain name!
Save and close the file. Now we can start Amavis.
sudo systemctl start amavisd
Enable auto-start at boot time.
sudo systemctl enable amavisd
Check its status:
systemctl status amavisd
Sample output:
● amavisd.service - Amavis mail content checker Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/amavisd.service; enabled; vendor preset: disabled) Active: active (running) since Thu 2020-11-19 01:21:26 EST; 8s ago Docs: http://www.ijs.si/software/amavisd/#doc Main PID: 18782 (/usr/sbin/amavi) Tasks: 3 (limit: 12502) Memory: 149.5M CGroup: /system.slice/amavisd.service ├─18782 /usr/sbin/amavisd (master) ├─18806 /usr/sbin/amavisd (virgin child) └─18807 /usr/sbin/amavisd (virgin child)
Hint: If the above command doesn’t quit immediately, press Q.
As you can see, Amavis is running. If it’s not running, you can check the logs with (sudo journalctl -eu amavisd).
Amavisd listens on 127.0.0.1:10024, as can be seen with:
sudo ss -lnpt | grep amavi
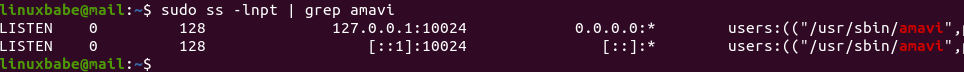
And it runs as the amavis user.
Step 2: Integrate Postfix SMTP Server With Amavis
Amavis works as an SMTP proxy. Email is fed to it through SMTP, processed, and fed back to the MTA through a new SMTP connection.
Run the following command, which tells Postfix to turn on content filtering by sending every incoming email message to Amavis, which listens on 127.0.0.1:10024.
sudo postconf -e "content_filter = smtp-amavis:[127.0.0.1]:10024"
Also, run the following command. This will delay Postfix connection to content filter until the entire email message has been received, which can prevent content filters from wasting time and resources for slow SMTP clients.
sudo postconf -e "smtpd_proxy_options = speed_adjust"
Then edit the master.cf file.
sudo nano /etc/postfix/master.cf
Add the following lines at the end of the file. This instructs Postfix to use a special SMTP client component called smtp-amavis to deliver email messages to Amavis. Please allow at least one whitespace character (tab or spacebar) before each -o. In postfix configurations, a preceding whitespace character means that this line is continuation of the previous line.
smtp-amavis unix - - n - 2 smtp
-o syslog_name=postfix/amavis
-o smtp_data_done_timeout=1200
-o smtp_send_xforward_command=yes
-o disable_dns_lookups=yes
-o max_use=20
-o smtp_tls_security_level=none
Then add the following lines at the end of the file. This tells Postfix to run an additional smtpd daemon listening on 127.0.0.1:10025 to receive email messages back from Amavis.
127.0.0.1:10025 inet n - n - - smtpd
-o syslog_name=postfix/10025
-o content_filter=
-o mynetworks_style=host
-o mynetworks=127.0.0.0/8
-o local_recipient_maps=
-o relay_recipient_maps=
-o strict_rfc821_envelopes=yes
-o smtp_tls_security_level=none
-o smtpd_tls_security_level=none
-o smtpd_restriction_classes=
-o smtpd_delay_reject=no
-o smtpd_client_restrictions=permit_mynetworks,reject
-o smtpd_helo_restrictions=
-o smtpd_sender_restrictions=
-o smtpd_recipient_restrictions=permit_mynetworks,reject
-o smtpd_end_of_data_restrictions=
-o smtpd_error_sleep_time=0
-o smtpd_soft_error_limit=1001
-o smtpd_hard_error_limit=1000
-o smtpd_client_connection_count_limit=0
-o smtpd_client_connection_rate_limit=0
-o receive_override_options=no_header_body_checks,no_unknown_recipient_checks,no_address_mappings
Save and close the file. Restart Postfix for the changes to take effect.
sudo systemctl restart postfix
Step 3: Integrate Amavis with ClamAV
Now that Postfix can pass incoming emails to Amavis, we need to install the ClamAV virus scanner and integrate it with Amavis, so incoming emails can be scanned by ClamAV.
Install ClamAV on CentOS 8/RHEL 8.
sudo dnf install clamav clamav-lib clamav-data clamav-update -y
There will be two systemd services installed by ClamAV:
[email protected]: the Clam AntiVirus userspace daemonclamav-freshclam.service: the ClamAV virus database updater
First, start the clamav-freshclam.service.
sudo systemctl start clamav-freshclam.service
Enable auto-start at boot time.
sudo systemctl enable clamav-freshclam.service
Check the status.
systemctl status clamav-freshclam
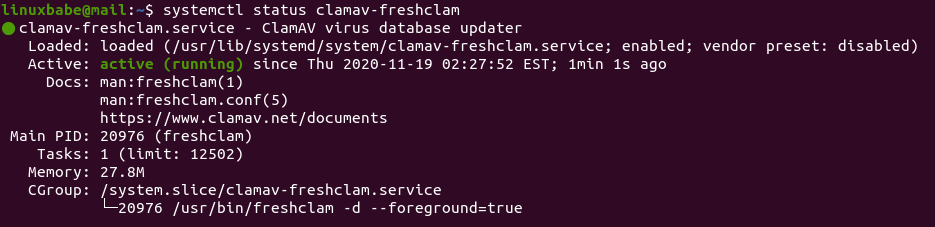
As you can see, it’s active (running) and uses 27.8 RAM on my mail server. Then check the journal/log.
sudo journalctl -eu clamav-freshclam
Output:
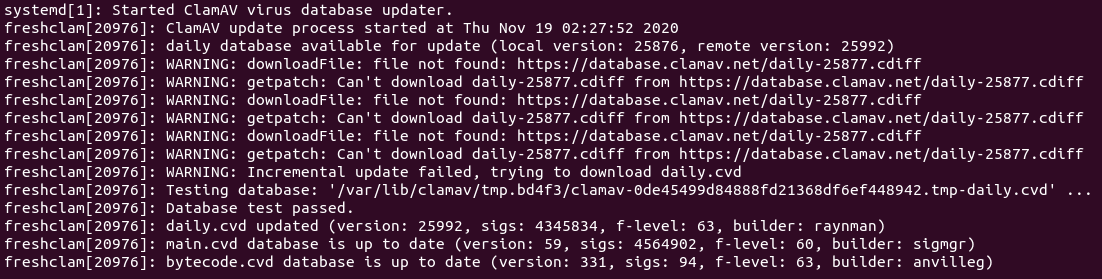
Hint: If the above command doesn’t quit immediately, press the Q key to make it quit.
We can see that freshclam downloaded 3 virus databases. CVD stands for ClamAV Virus Database.
- daily.cvd
- main.cvd
- bytecode.cvd
The clamav-freshclam.service will check ClamAV virus database updates once per hour.
Now we can start [email protected].
sudo systemctl start [email protected]
Enable auto-start at boot time.
sudo systemctl enable [email protected]
Check its status:
systemctl status [email protected]
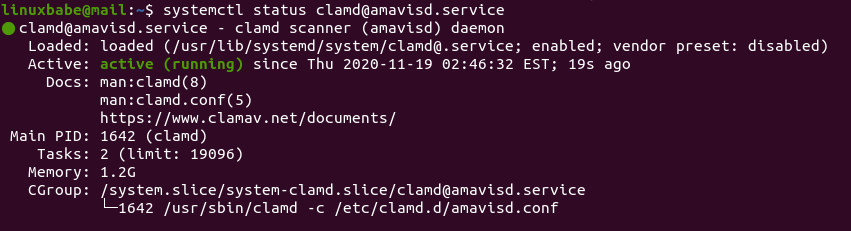
As you can see, it is running. By the way, it uses 1.2G RAM on my mail server. If your mail server doesn’t have enough RAM left, the service will fail.
Open the Amavis configuration file.
sudo nano /etc/amavisd/amavisd.conf
You can find the following line in this file, which enables virus-checking.
# @bypass_virus_checks_maps = (1); # controls running of anti-virus code
If you uncomment this line, virus-checking will be disabled.
There are lots of antivirus scanners defined in the @av_scanners section. ClamAV is the default. Amavis will call ClamAV via the /run/clamd.amavisd/clamd.sock Unix socket. ClamAV and Amvis both run as the amavis user.
Close the file and restart Amavis.
sudo systemctl restart amavisd
Check the logs.
sudo journalctl -eu amavisd
You can see that Amavis is now using ClamAV to scan viruses.
mail.linuxbabe.com amavis[1233432]: Using primary internal av scanner code for ClamAV-clamd mail.linuxbabe.com amavis[1233432]: Found secondary av scanner ClamAV-clamscan at /usr/bin/clamscan
Now if you send an email from other mail servers like Gmail to your own mail server and check the email headers, you can find a line like below, which indicates this email has been scanned by Amavis.
X-Virus-Scanned: Debian amavisd-new at linuxbabe.com
You should also check the mail log (/var/log/maillog) to find if there are any errors.
Step 4: Use A Dedicated Port for Email Submissions
ClamAV can scan both incoming and outgoing emails now. Amavis listens on port 10024 for both incoming and outgoing email messages. However, it’s a good practice to use a different port such as 10026 for email submissions from authenticated users.
Edit the Amavis main configuration file.
sudo nano /etc/amavisd/amavisd.conf
Find the following line.
$inet_socket_port = 10024; # listen on this local TCP port(s)
Add a # character at the beginning to comment it out.
#$inet_socket_port = 10024; # listen on this local TCP port(s)
Then find the following line.
# $inet_socket_port = [10024,10026]; # listen on multiple TCP ports
Remove the first # character to uncomment it, so Amavisd will also listen on port 10026.
$inet_socket_port = [10024,10026]; # listen on multiple TCP ports
Scrolling down a little bit, you can find the following line, which sets the “ORIGINATING” policy for port 10026.
$interface_policy{'10026'} = 'ORIGINATING';
Then you can find the following lines, which define the “ORIGINATING” policy.
$policy_bank{'ORIGINATING'} = { # mail supposedly originating from our users
originating => 1, # declare that mail was submitted by our smtp client
allow_disclaimers => 1, # enables disclaimer insertion if available
# notify administrator of locally originating malware
virus_admin_maps => ["virusalert@$mydomain"],
spam_admin_maps => ["virusalert@$mydomain"],
warnbadhsender => 1,
# forward to a smtpd service providing DKIM signing service
forward_method => 'smtp:[127.0.0.1]:10027',
# force MTA conversion to 7-bit (e.g. before DKIM signing)
smtpd_discard_ehlo_keywords => ['8BITMIME'],
bypass_banned_checks_maps => [1], # allow sending any file names and types
terminate_dsn_on_notify_success => 0, # don't remove NOTIFY=SUCCESS option
};
In the above lines, you can see that by default Amavis would forward emails to a SMTPD service providing DKIM signing servie. Postfix and OpenDKIM will take care of DKIM signing, so we need to comment out the forward_method directive.
# forward_method => 'smtp:[127.0.0.1]:10027',
Save and close the file. Next, we need to tell SELinux to allow Amavis to use port 10026. Install the following package, which provides the semanage command.
sudo dnf install policycoreutils-python-utils -y
Then set the port type of 10026 to amavisd_recv_port_t, so Amavis will be able to listen on port 10026.
sudo semanage port -m -t amavisd_recv_port_t -p tcp 10026
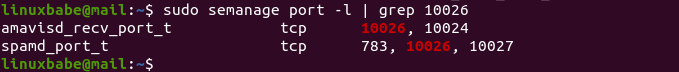
Check port 10026.
sudo semanage port -l | grep 10026
We can see that port 10026 can also be used by Amavisd.
Restart Amavis
sudo systemctl restart amavisd
Check its status to see if the restart is successful.
systemctl status amavisd
Next, edit the Postfix master configuration file.
sudo nano /etc/postfix/master.cf
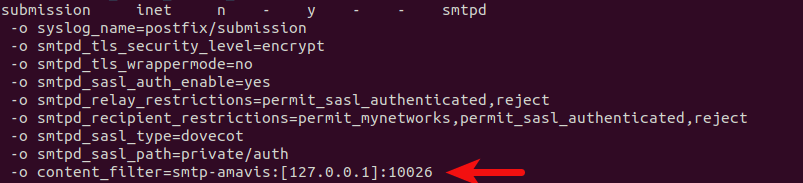
Add the following line to the submission service, so emails from authenticated SMTP clients will be passed to Amavis listening on port 10026. This line will override (-o) the content_filter paramter in /etc/postfix/main.cf file.
-o content_filter=smtp-amavis:[127.0.0.1]:10026
Like this:
If you have enabled the smtps service for Microsoft Outlook users, then you also need to add this line to the smtps service.
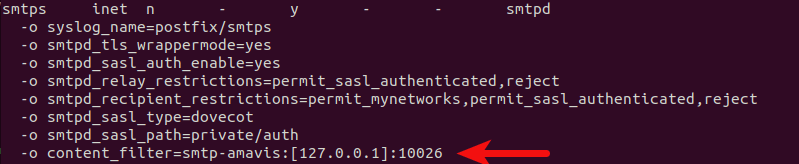
Save and close the file. Restart Postfix for the changes to take effect.
sudo systemctl restart postfix
Check its status to see if the restart is successful.
systemctl status postfix
Disabling Spam Filtering in Amavis
Spam filtering in Amavis is enabled by default. If you have followed my SpamAssassin tutorial, you don’t need to enable spam-checking in Amavis. If you enable it, each email will be checked twice by SpamAssassin.
To disable spam-checking in Amavis, edit Amavis configuration file.
sudo nano /etc/amavisd/amavisd.conf
Find the following line.
# @bypass_spam_checks_maps = (1); # controls running of anti-spam code
Remove the first comment character (#) to disable spam-checking.
@bypass_spam_checks_maps = (1); # controls running of anti-spam code
Save and close the file. Then restart Amavis.
sudo systemctl restart amavisd
Disabling DKIM in Amavis
Two common pieces of software that can do DKIM signing and verification on Linux are OpenDKIM and Amavis. I prefer to use OpenDKIM because it works better with OpenDMARC. So I won’t explain how to DKIM sign your email in Amavis.
By default, DKIM signing and verification are both enabled in Amavis. If you have OpenDKIM running on your mail server, then you can disable DKIM in Amavis.
sudo nano /etc/amavisd/amavisd.conf
Find the following two-line and change both 1 to 0, so Amavis won’t verify DKIM signatures for incoming emails or add DKIM signature for outgoing emails.
$enable_dkim_verification = 1; # enable DKIM signatures verification $enable_dkim_signing = 1; # load DKIM signing code, keys defined by dkim_key
Save and close the file. Then restart Amavis.
sudo systemctl restart amavisd
When receiving incoming emails, Postfix will call OpenDKIM via the sendmail milter interface to verify DKIM signatures, then pass the email to Amavis for virus-checking. When sending outgoing emails, Postfix will call OpenDKIM to sign the emails, then pass them to Amavis for virus-checking.
Improving Amavis Performance
By default, Amavis runs 2 processes. If you see the following lines in the mail log (/var/log/maillog), it means Amavis can’t process emails fast enough.
postfix/qmgr[1619188]: warning: mail for [127.0.0.1]:10024 is using up 4001 of 4008 active queue entries postfix/qmgr[1619188]: warning: you may need to reduce smtp-amavis connect and helo timeouts postfix/qmgr[1619188]: warning: so that Postfix quickly skips unavailable hosts postfix/qmgr[1619188]: warning: you may need to increase the main.cf minimal_backoff_time and maximal_backoff_time postfix/qmgr[1619188]: warning: so that Postfix wastes less time on undeliverable mail mail postfix/qmgr[1619188]: warning: you may need to increase the master.cf smtp-amavis process limit mail postfix/qmgr[1619188]: warning: please avoid flushing the whole queue when you have mail postfix/qmgr[1619188]: warning: lots of deferred mail, that is bad for performance
To improve performance, edit Amavis configuration file.
sudo nano /etc/amavisd/amavisd.conf
Find the following line. Change 2 to 4, which will make Amavis run 4 processes. If you have 10 CPU cores, you can change 4 to 10.
$max_servers = 2; # num of pre-forked children (2..30 is common), -m
Save and close the file. Then edit the Postifx master configuration file.
sudo nano /etc/postfix/master.cf
Find the smtp-amavis service definition, and change the process limit from 2 to 4.
smtp-amavis unix - - n - 4 smtp
-o syslog_name=postfix/amavis
-o smtp_data_done_timeout=1200
-o smtp_send_xforward_command=yes
-o disable_dns_lookups=yes
-o max_use=20
-o smtp_tls_security_level=none
Save and close the file. Then restart Amavis and Postfix for the changes to take effect.
sudo systemctl restart amavisd postfix
Now run the following command. You should see that there are 4 Amavis processes now.
sudo amavisd-nanny
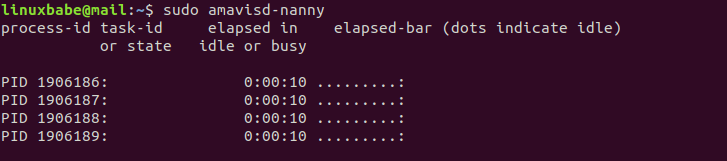
Press Ctrl C to stop amavisd-nanny.
Skipping Virus-Checking for Your Newsletters
If you use your mail server to send newsletters, and you enable Amavis and ClamAV, then lots of CPU and RAM resources will be used for virus-checking when you send newsletters to your subscribers. It could make your mail server unresponsive. You can skip virus-checking for your newsletters by using the method below.
Edit the Postfix master configuration file.
sudo nano /etc/postfix/master.cf
Add the following lines at the beginning of this file. This will enable smtpd on port 2525 of the localhost and it can accept client connections initiated from the same server. If there’s another process listening on port 2525, you can change 127.0.0.1:2525 to something else, like 127.0.0.1:2552. Note that the content_filter parameter is set to none, which means emails won’t be scanned by ClamAV.
127.0.0.1:2525 inet n - - - 1 smtpd -o syslog_name=postfix/2525 -o postscreen_greet_action=ignore -o content_filter=
Then add the following lines at the end of this file. Replace 12.34.56.78 with the mail server’s public IP address. This will create another Postfix submission daemon listening on port 10587. This is for client connections from another server. The content_filter parameter is also set to none.
12.34.56.78:10587 inet n - y - - smtpd
-o syslog_name=postfix/10587
-o smtpd_tls_security_level=encrypt
-o smtpd_tls_wrappermode=no
-o smtpd_sasl_auth_enable=yes
-o smtpd_relay_restrictions=permit_sasl_authenticated,reject
-o smtpd_recipient_restrictions=permit_mynetworks,permit_sasl_authenticated,reject
-o smtpd_sasl_type=dovecot
-o smtpd_sasl_path=private/auth
-o content_filter=
Save and close the file. Then Restart postfix.
sudo systemctl restart postfix
If your newsletter application runs on the mail server, then specify 127.0.0.1:2525 as the SMTP host, without SMTP authentication. If your newsletter application runs on a different server, then specify 12.34.56.78:10587 as the SMTP host, with SMTP authentication.
Wrapping Up
I hope this tutorial helped you set up Amavis and ClamAV on CentOS 8/RHEL 8 mail server. As always, if you found this post useful, then subscribe to our free newsletter to get more tips and tricks. Take care 🙂
Rate this tutorial
[Total: 1 Average: 5]