The drives on any system can either be mounted or unmounted. The mounted drives are the ones that are ready to be accessed at any time whereas the data residing on the unmounted drives can only be accessed after these drives are mounted. In the proceeding section of this article, we want to share with you the different methods of displaying all available drives on Linux.
Display all Drives on Linux
To display all of your drives on a Linux system, you can perform any of the following four methods:
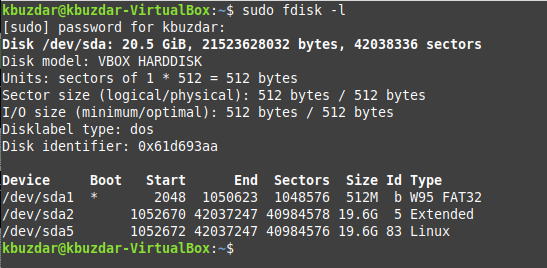
Method # 1: Using the “fdisk” Command
The “fdisk” command can be used to display the drives in Linux in the manner shown below:
$ sudo fdisk -l
![]()
The output produced by this command is shown in the following image:
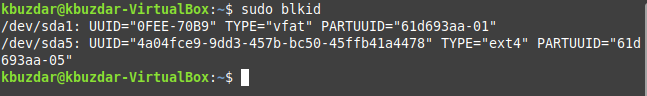
Method # 2: Using the “blkid” Command:
The “blkid” command can be used to display available drives in Linux in the manner shown below:
$ sudo blkid
![]()
The output produced by this command is shown in the following image:
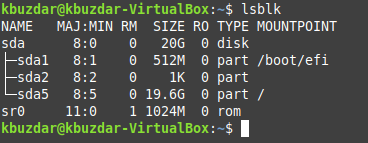
Method # 3: Using the “lsblk” Command:
The “lsblk” command can be used to display the system drives in Linux in the manner shown below:
$ lsblk
![]()
The output produced by this command is shown in the following image:
Method # 4: Using the “parted” Command:
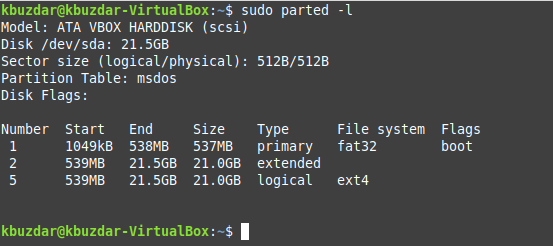
The “parted” command can be used to display the disk partitions in Linux in the manner shown below:
$ sudo parted -l
![]()
The output produced by this command is shown in the following image:
Conclusion
By picking out any of the four methods shared in this article, you can conveniently find out all the mounted and unmounted drives on your Ubuntu system. Once you have this information, you can always mount a drive out of these whenever you wish to access its contents.