Every user that is new to the Linux environment, must need to know about the basic directory navigation and file management commands. In Linux, each command is used for a particular purpose that performs well for the specified task. The tool ‘mc’ known as Midnight Commander is a file manager that is used for Linux terminal. It acts as a good front end for executing all commands related to file management.
In this article, you will learn how to manage files using commands like ls, cd, rm, etc., and how to install the Midnight Commander file manager on CentOS 8.
The following commands are used for file management on CentOS 8.
List files – using ls command
The ‘ls’ command is used to list directories and files of a directory. By default, the ‘ls’ command lists all files and directories of the current directory. You will use the following command to list items of the current directory:
$ ls
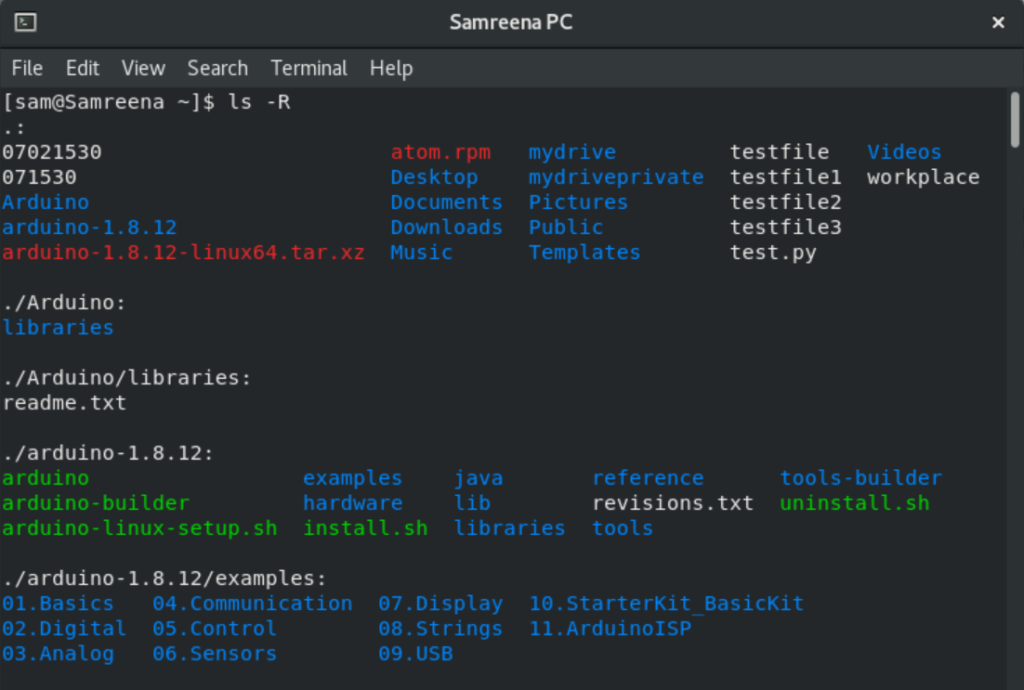
You can also list items of a directory in a recursive manner. To list files of a particular directory recursively, you will use the following command:
$ ls -R
You can also list files of another system’s directory. For this purpose, you will give the whole path of a particular directory with ‘ls’ command. For example, if you want to list your home directory files then you will use the ‘ls /home/sam’ that will list all files of the home directory.
Change directory – using cd command
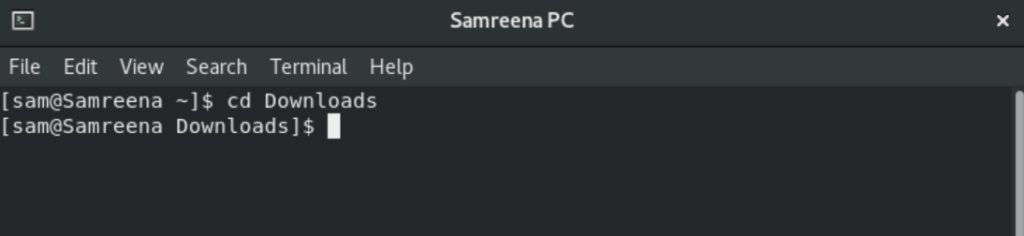
The ‘cd’ command is used to change from the current to another directory.
Cd command example
For example, if you want to move into ‘Downloads’ then you will use ‘cd Downloads’ that will take you in the Downloads directory.
Using cd command you can also move into a particular directory by giving the full path as ‘cd /home/sam/personal’.
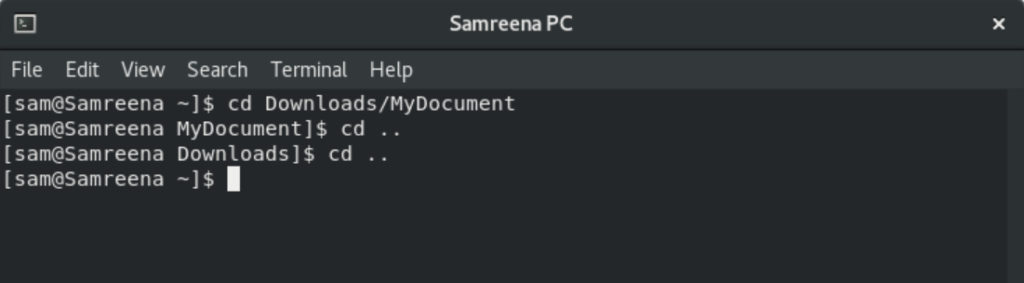
You will use ‘cd ..’ to move one step up to another directory.
Remove file – using rm command
The ‘rm’ command is used to remove or delete files. Before using this command, you must be careful because it will not ask the user for confirmation. The basic syntax of this command is given below:
$ rm filename
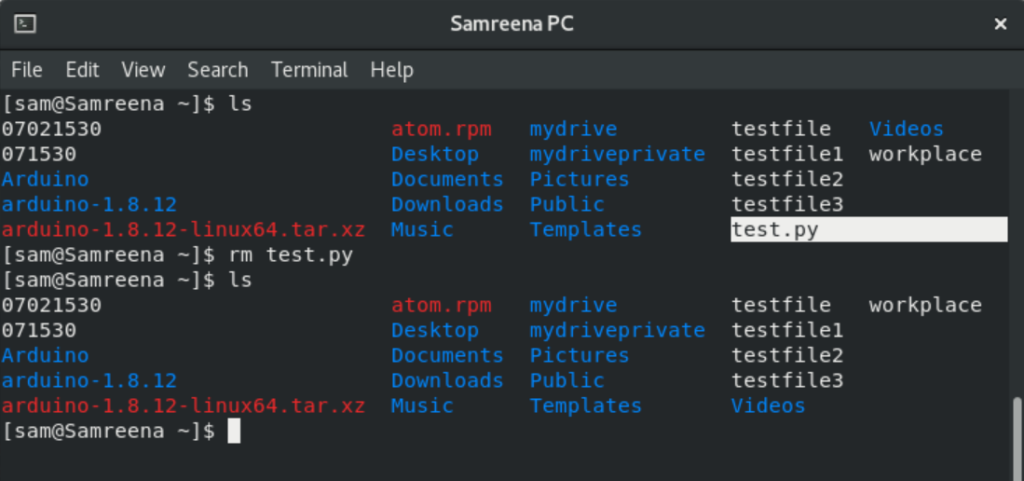
For example, if you want to remove a ‘test.py’ file then you will use ‘rm test.py’ to delete this file.
You can also remove or delete files from other directories. In this case, you will give the complete path of a file like ‘rm /home/sam/testfile’.
Move files – using mv command
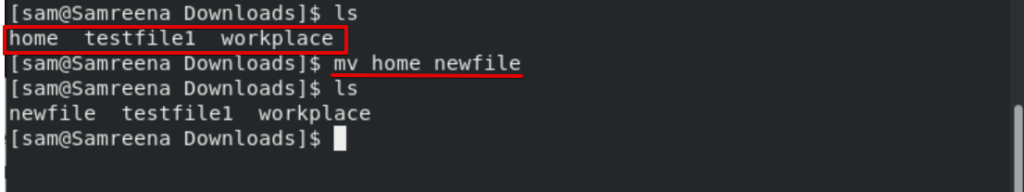
The ‘mv’ command is used to move files to a new location. This command is also used to rename a file. For example, you want to assign ‘newfile’ name to ‘home’ file then you will use the following command:
$ mv home newfile
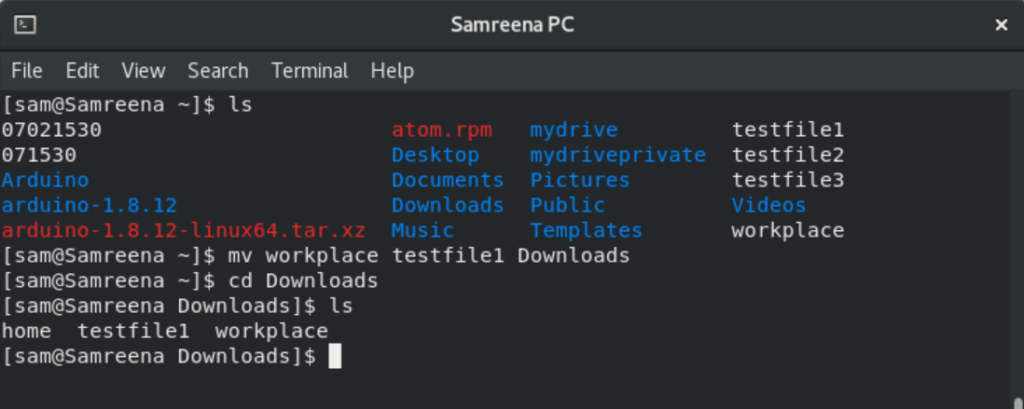
For example, if you want to move the ‘workplace’ and ‘testfile1’ files from home directory to ‘Downloads’ then you will use the following command:
$ mv workplace testfile1 Downloads
Similarly, you can also move a file to other directories to specify the full path like ‘mv newfile /home/sam’.
Copy files – using cp command
The cp command is used to make a copy of the file in another directory instead of moving.
$ cp filename Directoryname
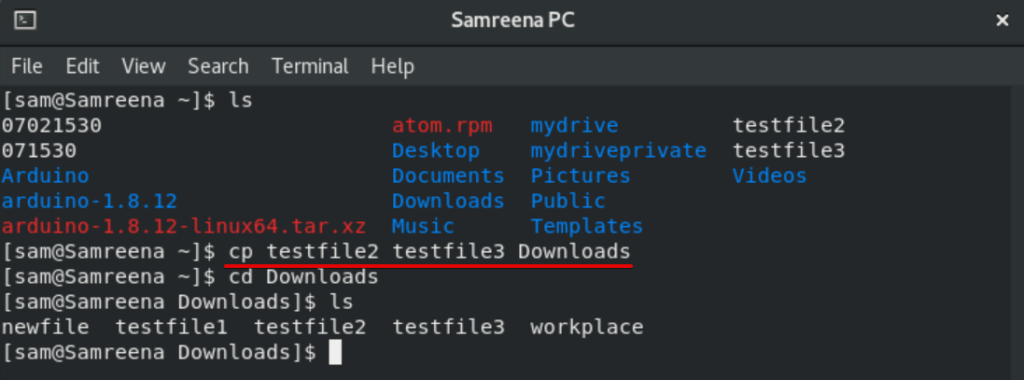
For example, if you want to generate the copy of ‘testfile2’ and ‘testfile3’ in ‘Downloads’ from home directory then you will use the following command:
$ cp testfile2 testfile3 Downloads
Create a new directory – using mkdir command
The ‘mkdir’ command is use to make a new directory.
For example, if you want to create a new directory of ‘Samreenatasks’ in the current directory then you will type the following command:
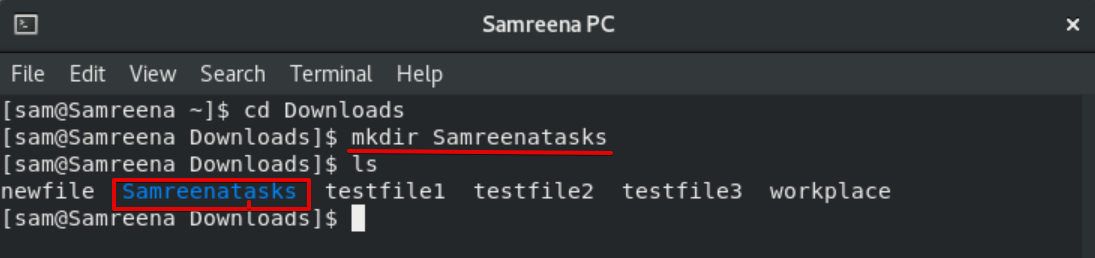
$ mkdir Samreenatasks
Create Symlinks – using ln command
The ‘ln’ command is used to create links. You can create a symbolic link using the following command:
$ ln -sf ~/bin/topprocs.sh topps.sh $ ls -l topps.sh
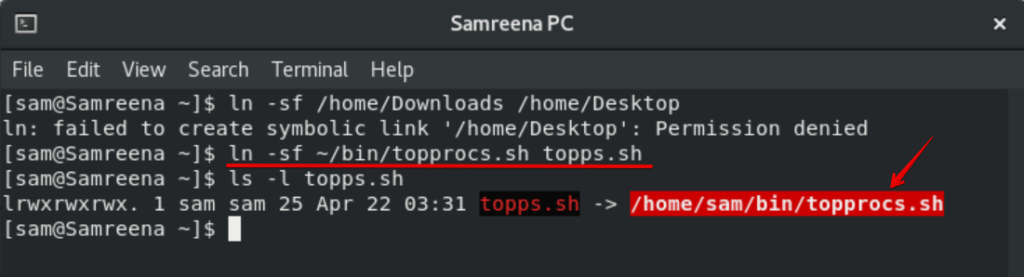
For example, you want to create a symbolic link with the name ‘topps.sh’ to the file ‘topprocs.sh’. Here ‘-sf’ is used that will force you to create a new link.
Change permission – Using chmod command
The chmod command is used to change permission on a file. The basic syntax is given below:
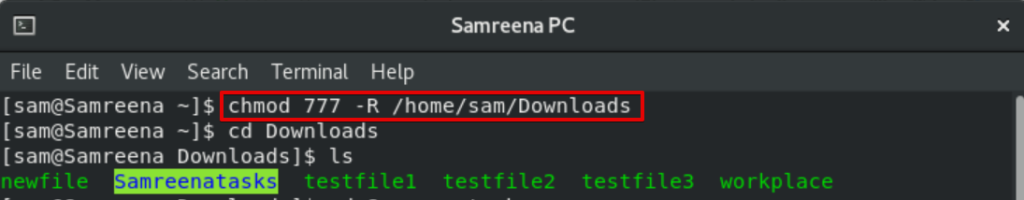
$ chmod 777 -R directory_name
Midnight Commander – mc file manager
You can also install the ‘mc’ file manager on your system. For this purpose, first, you will log in as the root user on your system.
Then, Install mc file manager on your system using yum command:
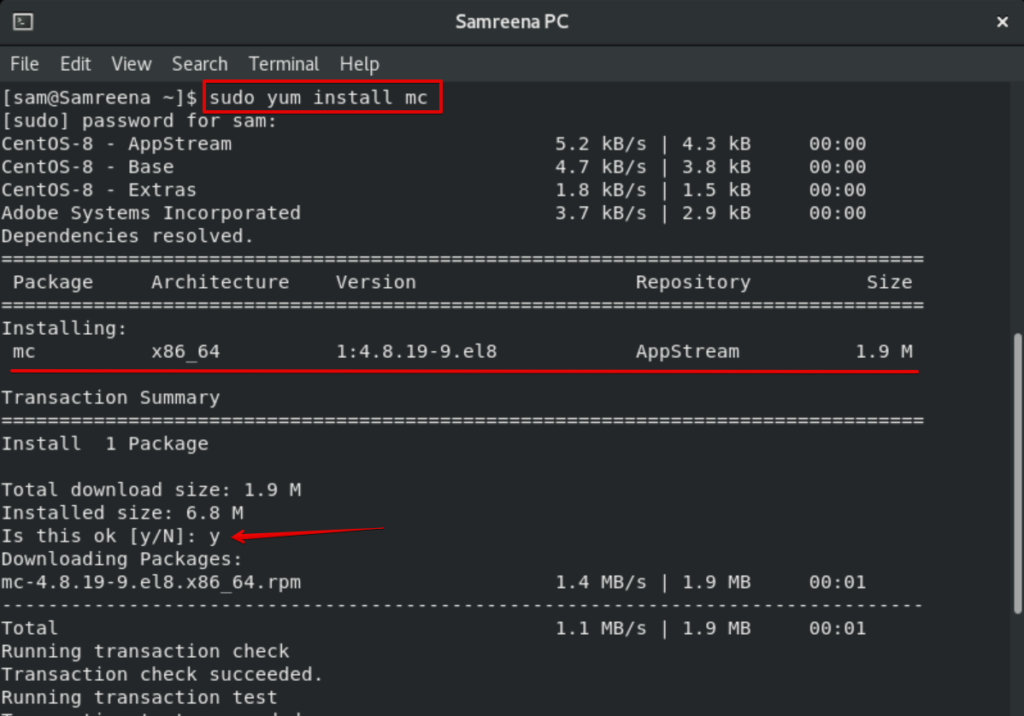
This process will take some time. During the installation, a confirmation prompt will be displayed in the terminal. You will press ‘y’ to proceed further. After that, the remaining installation will complete on your system.
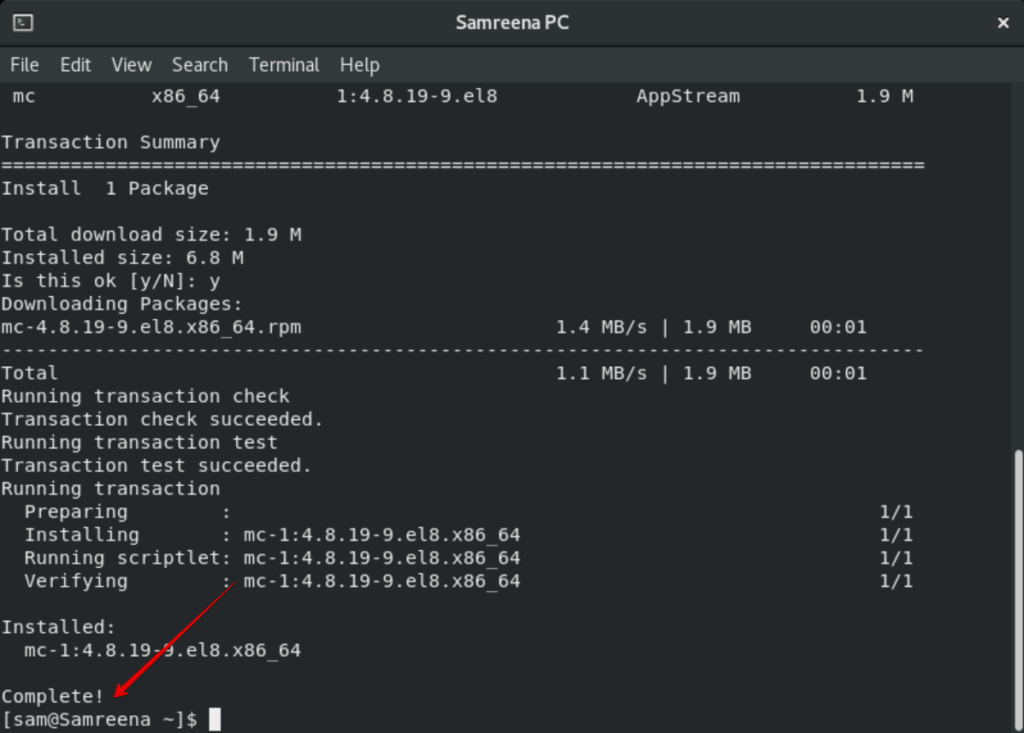
After completing the installation of the Midnight Commander, you will type ‘mc’ on the terminal to open the interface of mc file manager.
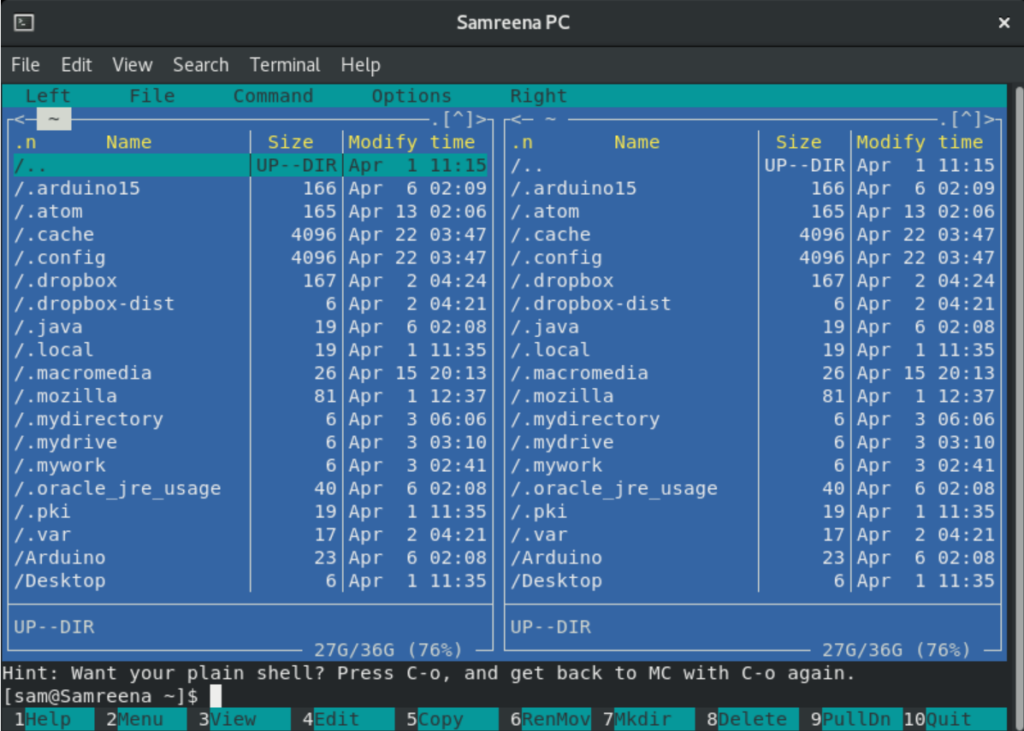
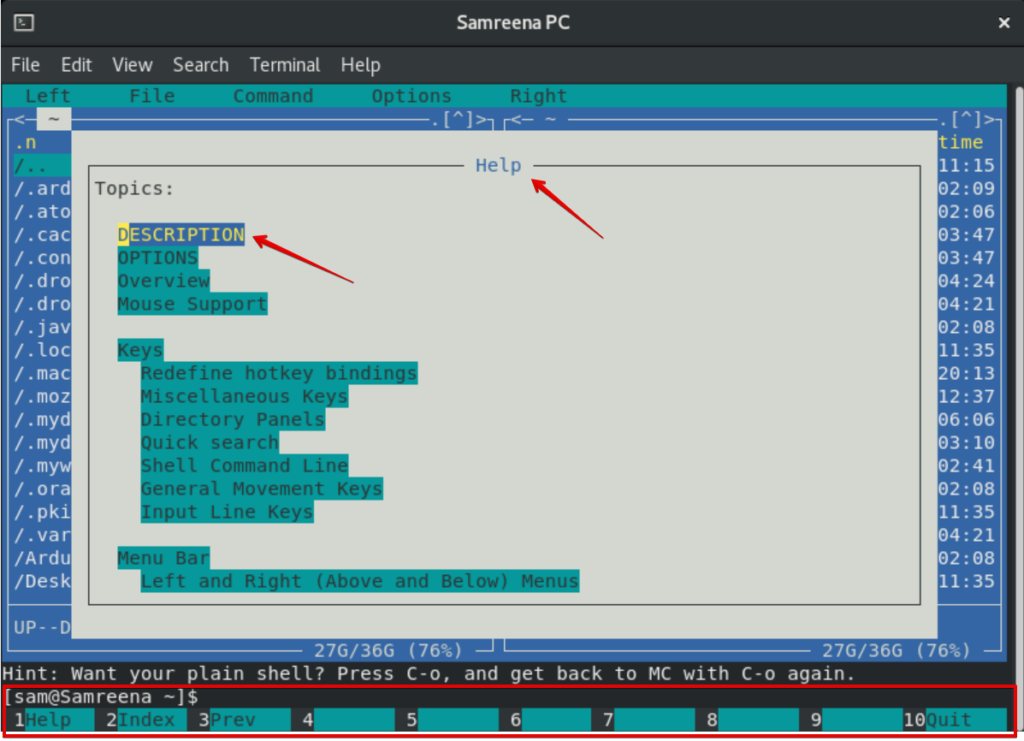
Now, you will navigate between the options using arrow keys. You can open help window using ‘Alt 1’ and can use more keys according to your requirements.
Conclusion
In this article, you have learned how to manage files and directories using the terminal and how to install midnight commander tool on CentOS 8. I hope this article would help you in the future. You can also explore more features of the mc file manager.