Apache Cassandra is an open-source distributed database developed for cloud computing. It provides a highly available and scalable database service with no single point of failure and no manual tuning.
Apache Cassandra is one of the most popular databases used in artificial intelligence to help create robots. With the ability to scale up quickly using commodity hardware, Cassandra could become one of the primary data storage systems that will power future robotic data management devices.
Apache Cassandra is a NoSQL database. With the addition of the Apache Thrift interface, Cassandra can be used to store and manage data without the use of SQL, while allowing developers to use familiar application development protocols like REST and Thrift.
Cassandra was primarily developed by Facebook engineer Prashant Malik. The database was named after the wife of a co-founder of Facebook, who died in a car accident in 2008. It is built on Google’s BigTable architecture, with support for distribution, replication, failure detection and load balancing using Apache ZooKeeper.
In Cassandra, data is spread across a cluster of servers. It has no single point of failure and can tolerate the loss of any number of machines without losing data. If needed, the total capacity of the system can be increased simply by adding more machines. Cassandra is designed to handle frequent failures and arbitrary machine loss very well at the cost of write availability while a repair is ongoing.
There are many benefits of using Apache Cassandra as a NoSQL database. But, it can be difficult to install and get started. In this tutorial, We will show you how to get started with Cassandra on your own Debian 11 server and make it as simple as possible.
You will learn how to create a cluster of Apache Cassandra on your computer. Also, you will learn how to use the client program ‘cqlsh’ to interact with the Cassandra database that you have installed on your computer.
After reading this tutorial, you will be able to install and use Cassandra on your own computer with ease.
Prerequisites
In order to complete this tutorial, you will need an Ubuntu 20.04 or Debian 11 server with the following specifications:
- Minimum 2GB of RAM, 2 CPUs at 2.0 GHz each. At least 40 GB of hard disk space for the installation.
- A non root-user with sudo privileges is set up on your server.
Updating Your System
First of all, make sure that you are up to date by issuing the following command on your server.
sudo apt update -y && sudo apt upgrade -y
Next, install the necessary packages required for Cassandra.
sudo apt install build-essential binutils bsdmainutils gnupg2 curl -y
Installing Java (JDK)
Next, we are going to install the Java Development Kit (JDK) on your server.
Java Development Kit (JDK) contains a compiler and tools for developing Java programs.
It is required to run the Cassandra client program cqlsh and thus the Cassandra server. By default, cqlsh looks for the Java Runtime Environment (JRE) installed on your computer. But sometimes, it can be hard to install JRE on Ubuntu or Debian-based systems as they are installed by default.
In this demo, we will install the official stable OpenJDK 11 JDK. OpenJDK is the official stable OpenJDK release from Oracle and the best alternative of JRE, which won’t let you down if you wish to use the JDK for developing your next great app.
Run the command below to install openjdk-11-openjdk on your server.
sudo apt install openjdk-11-jre -y
After installation, run the command below to test it to ensure that it has been installed properly.
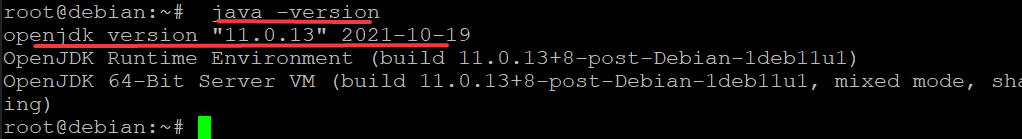
java -version
-version is the built-in command of the terminal which shows you the version of Java installed on your system. If you see the version number as shown below, it means you have successfully installed this JDK.
Installing Apache Cassandra NoSQL DB on Debian 11
Now that we have updated our system and installed the necessary packages, we are ready to install Cassandra on our server.
By default, the base repository of Debian 11 does not include Cassandra. In order to install Cassandra, we will have to add the official Cassandra repository from the Cassandra developer.
The official Cassandra repository contains the latest stable releases of Cassandra, its dependencies and its add-ons.
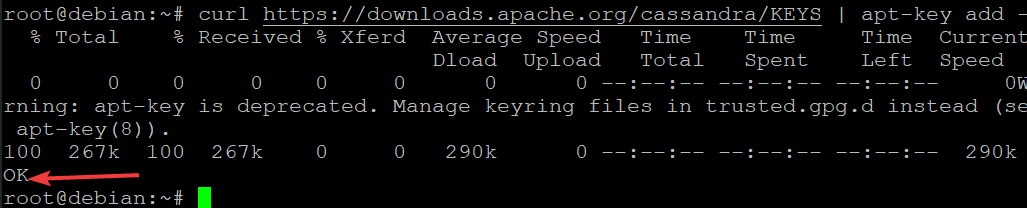
Run the command below to add the authentication key of the official Cassandra repository. This command adds the authentication key of the official Cassandra repository to your system’s APT keyring.
Adding an authentication key prevents unauthorized individuals from adding a malicious repository that contains a backdoored version of Cassandra or malware. It also verifies that you are accessing the official repository and not an impersonating repository.
curl https://downloads.apache.org/cassandra/KEYS | apt-key add -
You will get an OK message if the authentication key has been successfully added.
Now, add the official Cassandra repository to your system’s APT sources list. This command will add the official Cassandra repository to your system’s APT sources list. The GPG key information that is used to sign packages is automatically retrieved from keyserver network at this point.
echo "deb https://downloads.apache.org/cassandra/debian 40x main" | tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list.d/cassandra.list
After adding the official Cassandra repository to your system, run the command below to update your APT sources list.
sudo apt update -y
After you have updated your APT sources list, run the command below to verify if the official Cassandra repository is properly added to your system’s APT sources list.
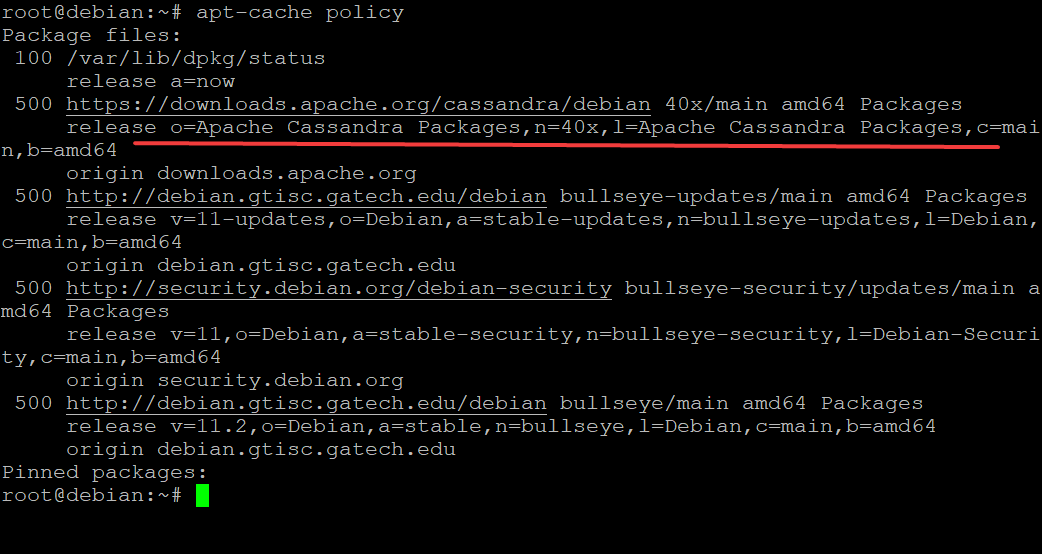
apt-cache policy
You will get an output similar to the one below. You can see that the repository is properly added to your system’s APT sources list. You should ensure that the version of the repository is shown as 40x in the output before you proceed to the next step.
Now, you can install Cassandra using the command below in your terminal or command prompt.
sudo apt install cassandra -y
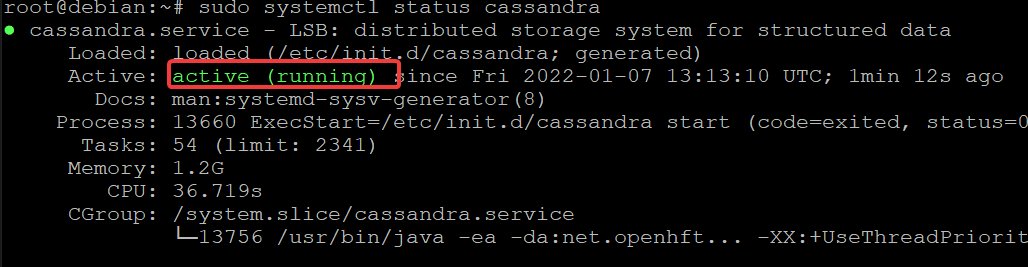
After installation, run the following command to check if Cassandra is properly installed on your system. You will get the status of your installed Cassandra.
sudo systemctl status cassandra
Testing Apache Cassandra
Now that you have successfully installed Cassandra, you are ready to test it. So we will start with testing the Cassandra server using nodetool. Nodetool is a utility that is used to diagnose problems with your Cassandra installation.
It reads information from Cassandra about what nodes are live, how many replicas there should be for each column family etc. It then prints out the information it gets from Cassandra and compares this with what you’d expect to see, given the schema. It tries to catch basic configuration problems.
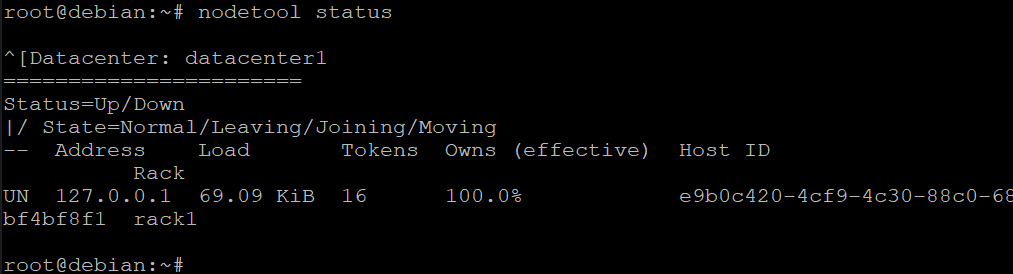
Run the nodetool status command to check errors and warnings about your installation.
nodetool status
You will get an output similar to the one below. If there are no errors, you have successfully installed Cassandra on your server.
You can also use the cqlsh client to test Cassandra. cqlsh is the official Cassandra client program bundled with Cassandra. In this demo, we will continue with testing the Cassandra on your server by using cqlsh to change the default name of the cluster on your system. And then recheck the name of the cluster.
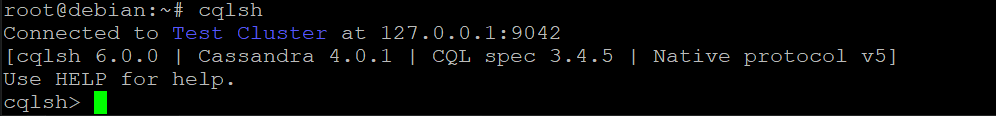
Run the cqlsh command below to log in to your Cassandra server.
cqlsh
You will see a screen similar to the one below.
In order to change the name of the cluster on your system, add in the query below at the prompt and press Enter.
Type exit and press Enter to quit cqlsh.
Open the /etc/cassandra/cassandra.yaml file in a text editor.
sudo nano /etc/cassandra/cassandra.yaml
Find the cluster_name: ‘Test Cluster’ line and change the name to Vitux. Save and exit the file by typing Ctrl O followed by Enter, and then Ctrl X to exit.
Before

After

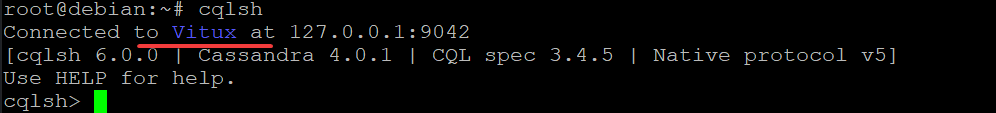
Now that your cluster is named Vitux, recheck the cluster name on your server.
cqlsh
If you can see that the name of the cluster changed to Vitux ton our system, it means that you have successfully changed the name of your cluster by using Cassandra’s cqlsh client in your terminal.
Conclusion
In this article, we have shown how to install Cassandra on a Debian 11 server. And how to test the installation by logging in to the system using cqlsh and changing the name of the cluster from Test Cluster to Vitux. If you want to learn more about Cassandra, visit its official website.