Ternary operator can be used as the alternative of ‘if-else’ and ‘if-else-if’ statements. It is called a ternary operator because it takes three operands to do any task. If the conditional expression that is used in a ternary statement returns true, then it executes a particular statement; otherwise, it executes another statement. The ‘?’ and ‘:’ symbols are used to define the ternary statement. The ternary operator is better to use for solving a very simple task in place of ‘if’ statement. Different uses of the ternary operator in java are shown in this tutorial.
Syntax:
Here, if the conditional statement returns true, then it will execute the statement defined in the left side of the ‘:’, and if it returns false, then it will execute the statement defined in the right side of the ‘:’.
Example-1: Use of the ternary operator with a single condition
The following example shows the very simple use of a ternary operator that can be used in the replacement of the ‘if-else’ statement. An integer value will be taken as input, and the ternary operator is used to check the value is greater than or equal to 80 or not. If the ternary condition returns true, then it will return the grade; otherwise, it will calculate how many marks are required to get 80 and return to the message variable that is printed later.
//Import Scanner package
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ternary1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a Scanner object
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print(“Enter your marks : “);
// Take marks from the user
int marks = in.nextInt();
// Store the string value based on an input value
String message = (marks >= 80) ? “Your grade is A “ : “You need “ (80–marks)
” to get A “;
System.out.println(message);
//Close the scanner object
in.close();
}
}
Output:
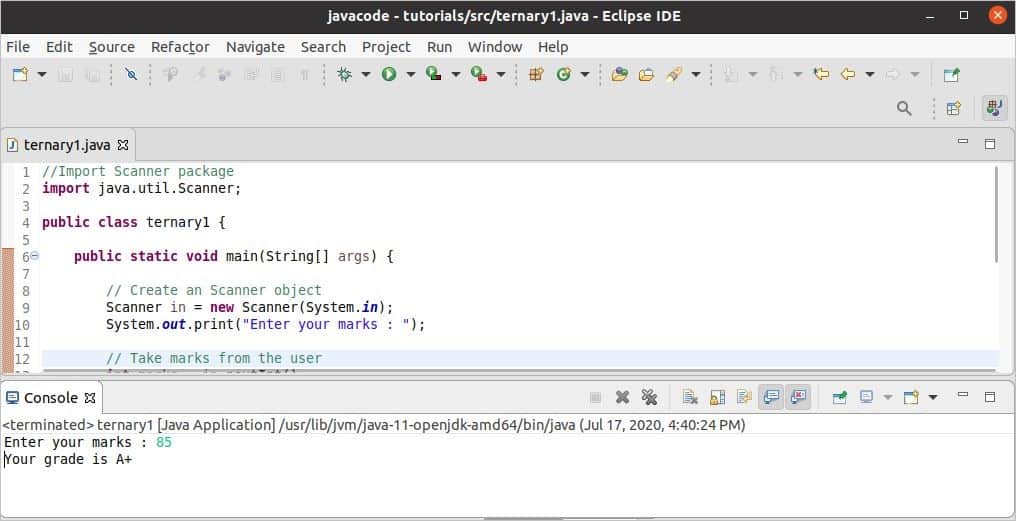
After running the code, 85 is taken as input that is more than 80. So, the grade value is printed here.
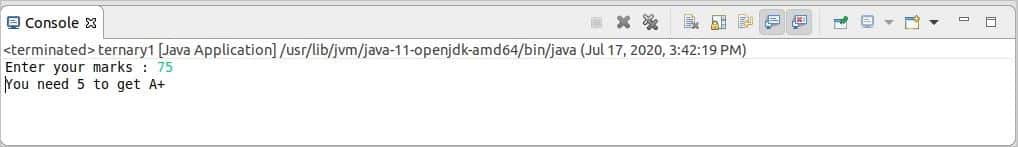
When 75 is taken as input, then the ternary condition returned false and, it calculated how many marks are required to get A and printed.
Example-2: Use of the ternary operator with multiple conditions
The following example shows the use of a ternary operator with two conditions, and if both conditions return true, then it will return a particular text; otherwise, it will return another text to val variable that will print later.
public class ternary2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Assign a string value
String name = “Abrar Fahad”;
//Asign a numeric value
int id = 22;
/* Store the string value based on
* the return value of the condition
*/
String val = (name.equals(“Abrar Fahad”) && id == 22) ?
“Your are selected” : “You are not selected”;
//Print the variable
System.out.println(val);
}
}
Output:
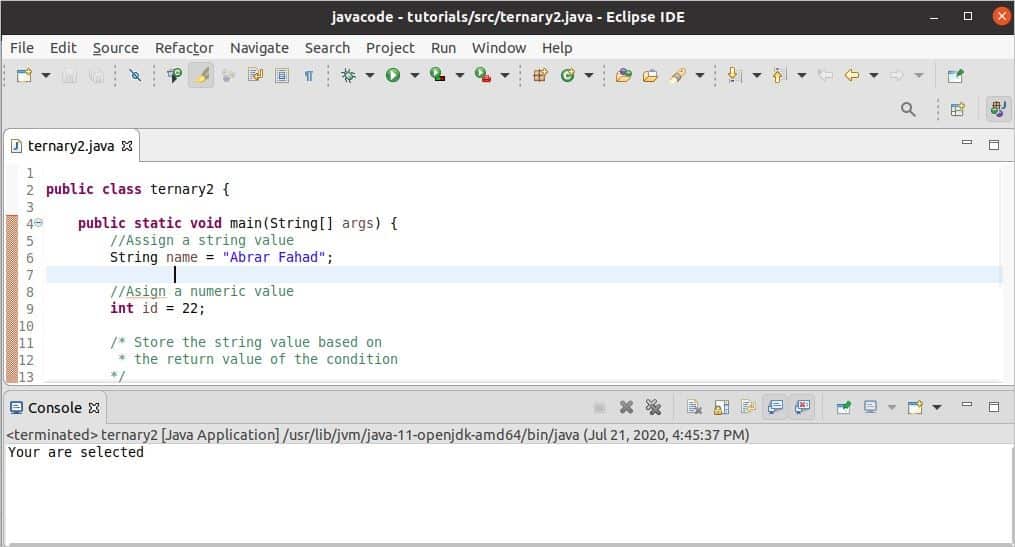
According to the code, the ternary condition will return true, and the following output will appear after executing the code.
Example-3: Use of the ternary operator to find the maximum value
Finding the maximum value between two numbers by using the ternary operator is shown in the following example. Two integer values will be taken from the users and compared in the ternary condition to find out the maximum value. Next, the maximum value will be printed with the formatted text.
//Import Scanner package
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ternary3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create an Scanner object
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print(“Enter a number : “);
// Take the first number
int num1 = in.nextInt();
System.out.print(“Enter a number : “);
// Take the second number
int num2 = in.nextInt();
// Store maximum value
int max_val = (num1 > num2) ? num1 : num2;
//Print maximum value
System.out.println(“The maximum number is: “ max_val);
//Close the scanner object
in.close();
}
}
Output:
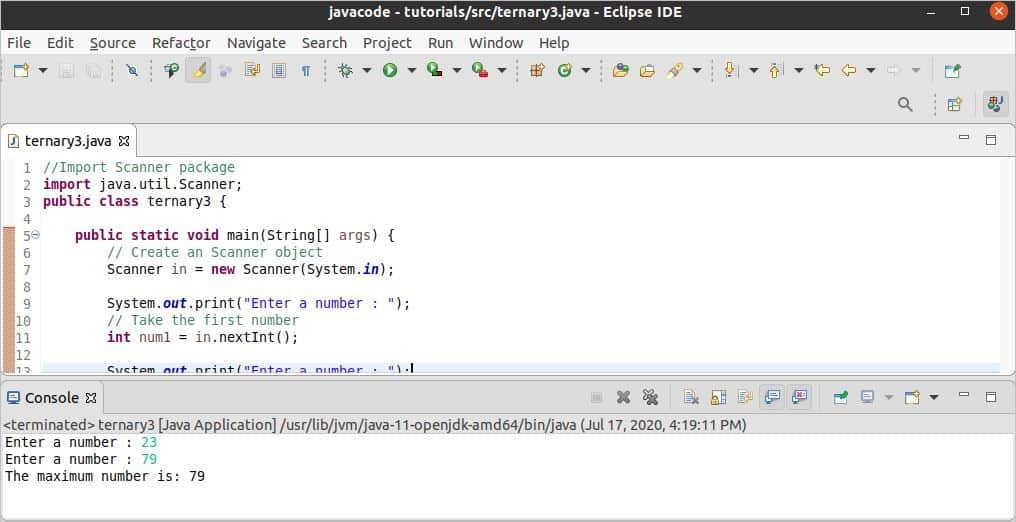
23 and 79 are taken as input after executing the code, and the maximum value is printed.
Example-4: Use of the nested ternary operator
Nested ternary operator can be used as the alternative of ‘if-else-if’ statement. The use of the nested ternary operator is shown in the following example. Here, an integer value will be taken as input and stored to the marks variable. The value of marks will be checked in the first ternary condition, and if it returns false, then it will check in the second ternary condition and so on. If all ternary conditions return false, then it will return the last text of the ternary statement. The grade variable is used to store the return value of the ternary expression that will print later as output.
//Import Scanner package
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ternary4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a Scanner object
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
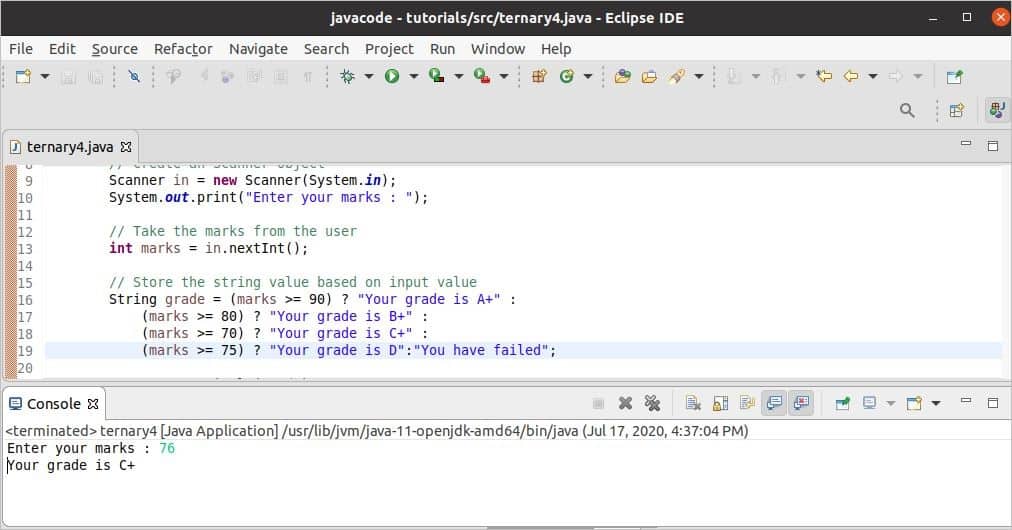
System.out.print(“Enter your marks : “);
// Take the marks from the user
int marks = in.nextInt();
// Store the string value based on the input value
String grade = (marks >= 90) ? “Your grade is A “ :
(marks >= 80) ? “Your grade is B “ :
(marks >= 70) ? “Your grade is C “ :
(marks >= 75) ? “Your grade is D”:“You have failed”;
System.out.println(grade);
//Close the scanner object
in.close();
}
}
Output:
76 is taken as input after running the code, and the third condition of the ternary operator became true based on the input value, and the corresponding text is printed.
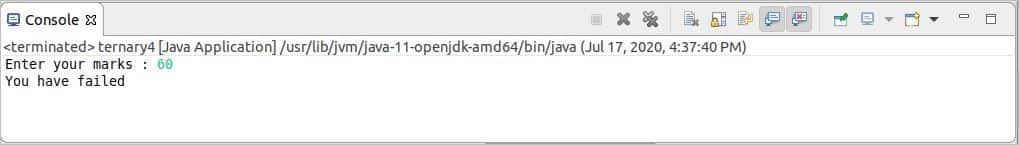
Next, 60 is taken as input, and all ternary conditions returned false. So, the last text of the ternary expression is printed.
Conclusion:
Using a ternary operator in place of ‘if-else’ and ‘if-else-if’ makes the code short and efficient in many cases. So, it is better to use it to solve simple problems. The different uses of ternary expression are explained in this tutorial by using simple examples. I hope the concept of the ternary operator and how this can be used in Java code will be cleared after reading this tutorial.
About the author

Fahmida Yesmin
I am a trainer of web programming courses. I like to write article or tutorial on various IT topics. I have a YouTube channel where many types of tutorials based on Ubuntu, Windows, Word, Excel, WordPress, Magento, Laravel etc. are published: Tutorials4u Help.